Notice: There is no legacy documentation available for this item, so you are seeing the current documentation.
The PushEngage React Native SDK simplifies the integration of push notifications in your React Native apps, offering seamless support for Android and iOS. We offer three frameworks for implementing app push notifications: React, Native, and Flutter. You can find guides for Native Android, iOS and Flutter app push notifications for further assistance.
In this guide, we will walk through setting up the PushEngage React Native SDK to enable push notifications on both Android and iOS.
Before You Start
Here is a list of things you would require
- A React Native project & turbo module support. If you do not have an account, you can sign up here.
- Firebase account with Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) setup for Android.
- An Apple Developer account to configure Apple Push Notification (APN) services for iOS.
Installing the PushEngage React Native SDK
You can install the PushEngage React Native SDK using either npm or yarn
npm install @pushengage/pushengage-react-nativeFor React Native 0.77.0 or Earlier
If you are using React Native version 0.77.0 or earlier, use the version 0.0.1 of the SDK as shown below:
npm install @pushengage/[email protected]Setting Up Android
Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) Setup
To enable push notifications for Android, you’ll need to configure Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM)
1. Access the Firebase console using your Google account.
2. Click on “Add Project” to create a new project, or select an existing project from your list. If you’re using an existing project, proceed directly to step 4.

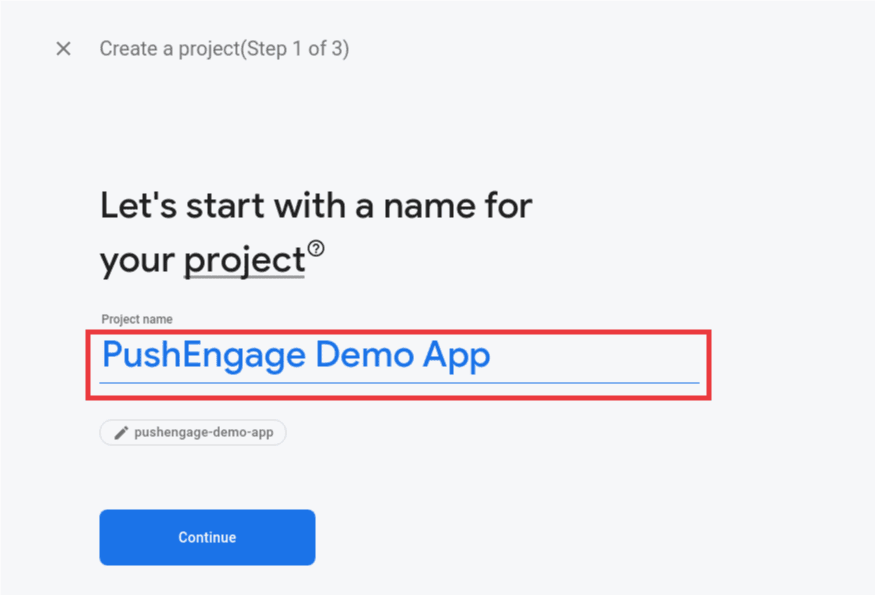
3. Enter a name for your project and click Continue. Complete the setup process by clicking “Create project” on the final screen.
4. In your Firebase project dashboard, click on the Android icon to add an Android app.

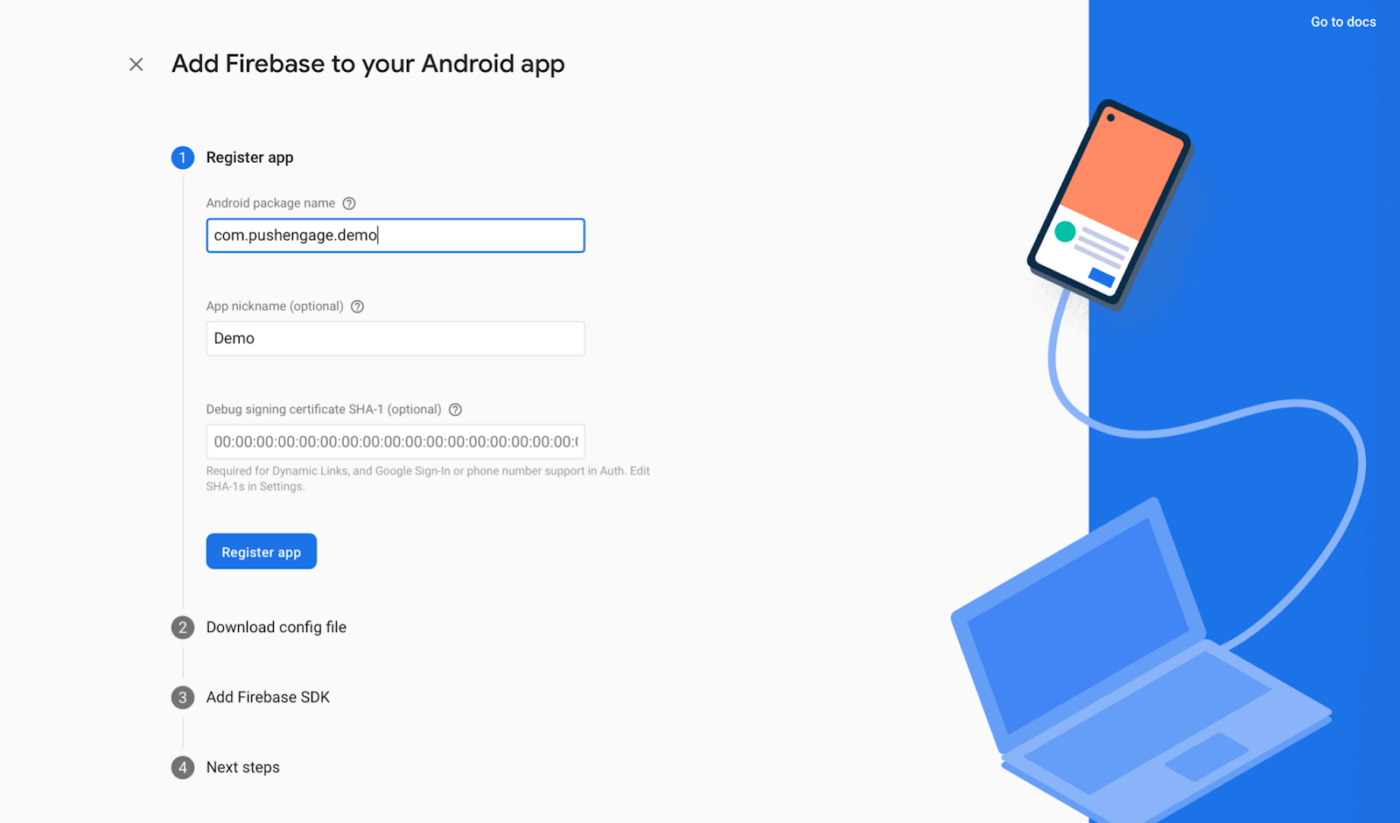
5. Enter your Android app’s package name (found in android/app/build.gradle under the android block) and provide an app name. Click Register when done.
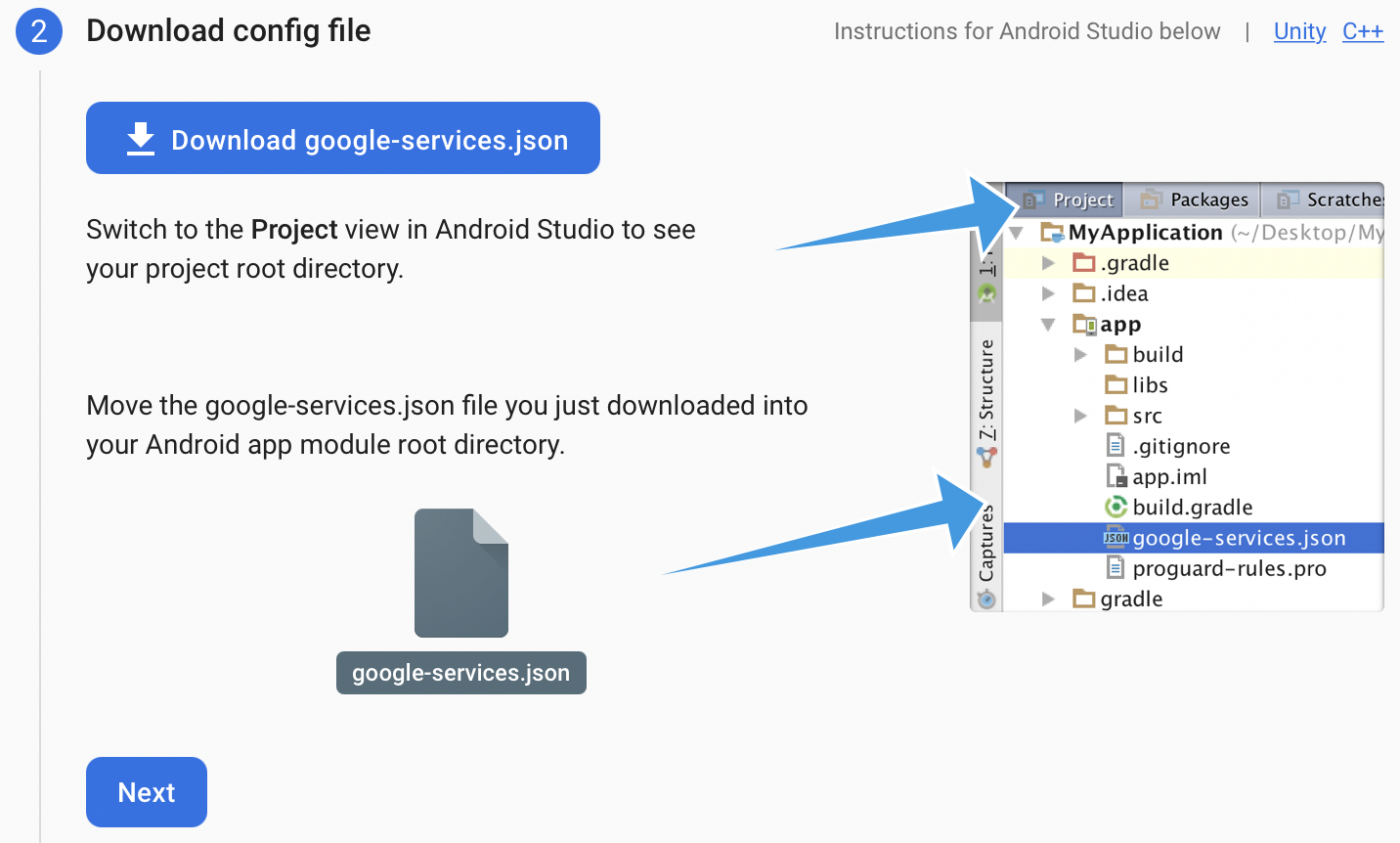
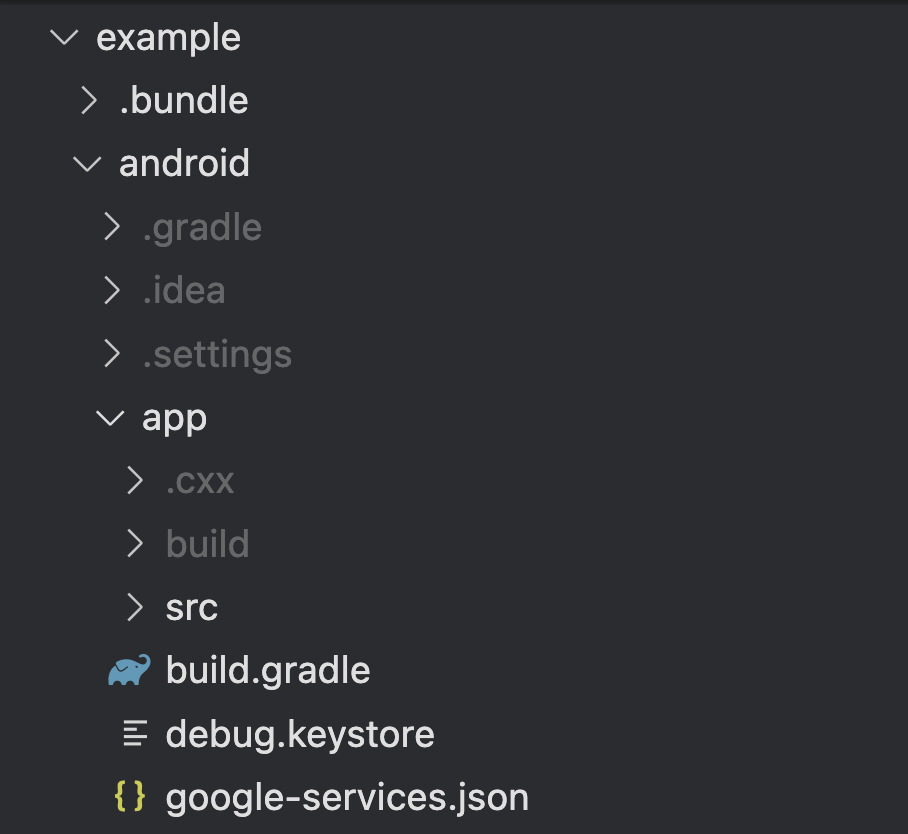
6. Download the google-services.json file and place it in the root of your Android app module at android/app/.
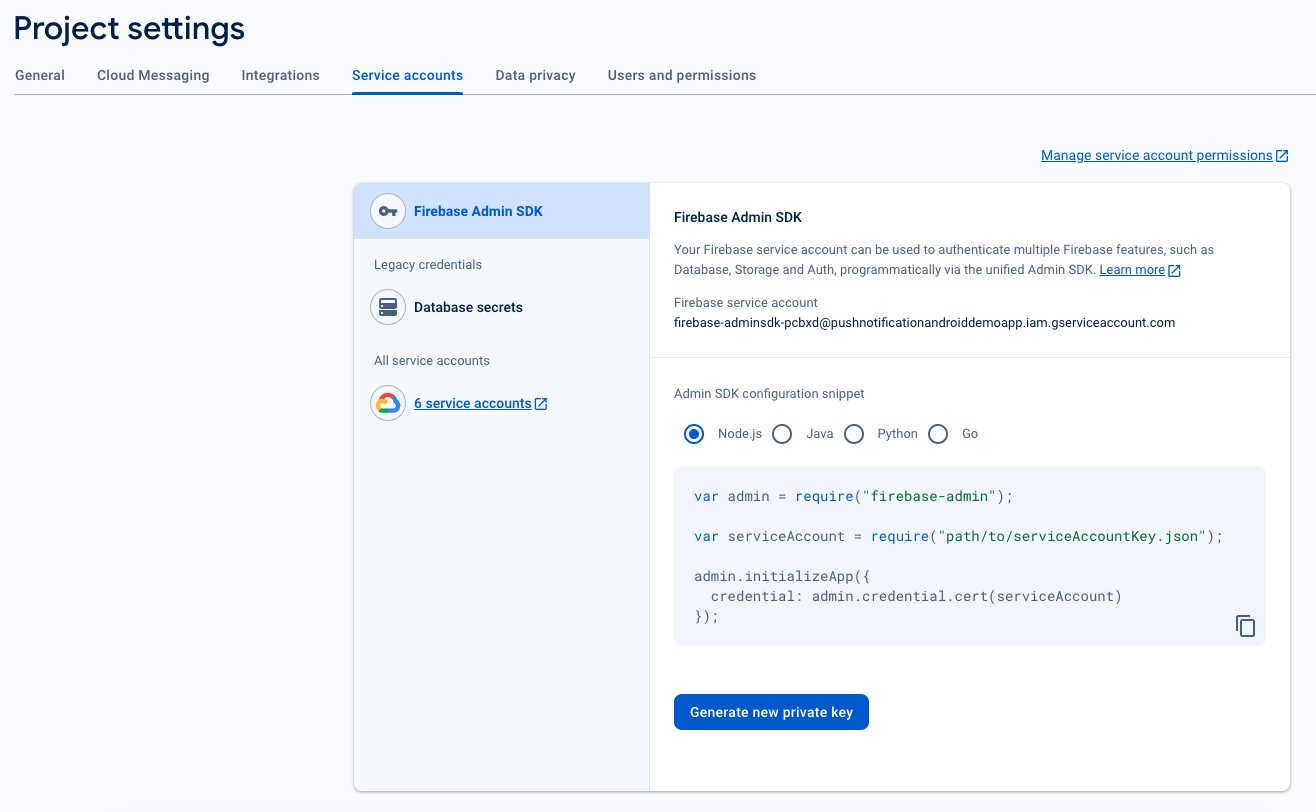
7. Generate Service Account JSON
- In the Firebase console, click the Settings icon next to “Project Overview” in the top left, then select Project settings.
- Navigate to the Service accounts tab.
- Click Generate new private key, and download the .json file.
- Keep this file safe as you will need it for the PushEngage dashboard setup.
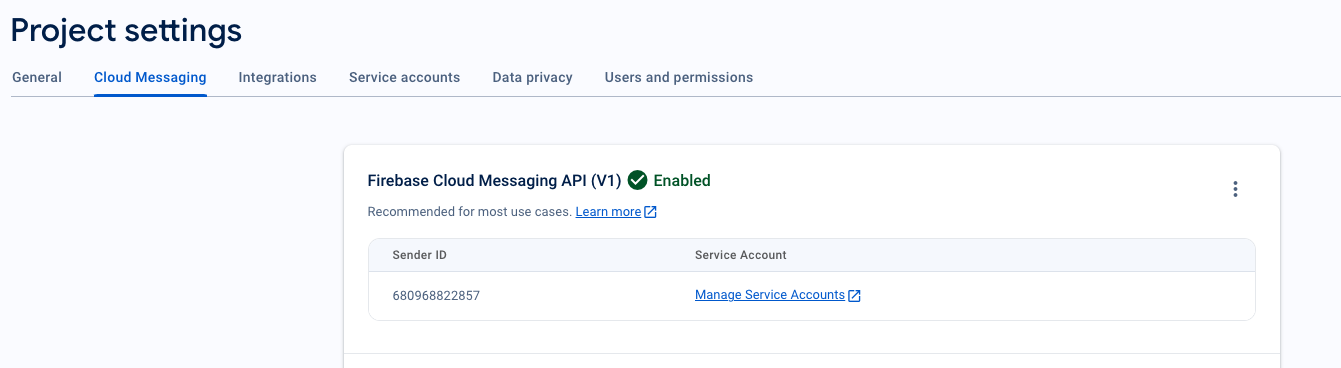
8. Retrieve Sender ID
- In the Firebase console, click the Settings icon next to Project Overview in the top left and select “Project settings.”
- Select the Cloud Messaging tab, Here, you’ll find the Sender ID, which is needed for PushEngage SDK initialization.
Integrate FCM with PushEngage
To seamlessly integrate FCM details with the PushEngage Dashboard, you can follow below steps.
1. Access your PushEngage account by logging in
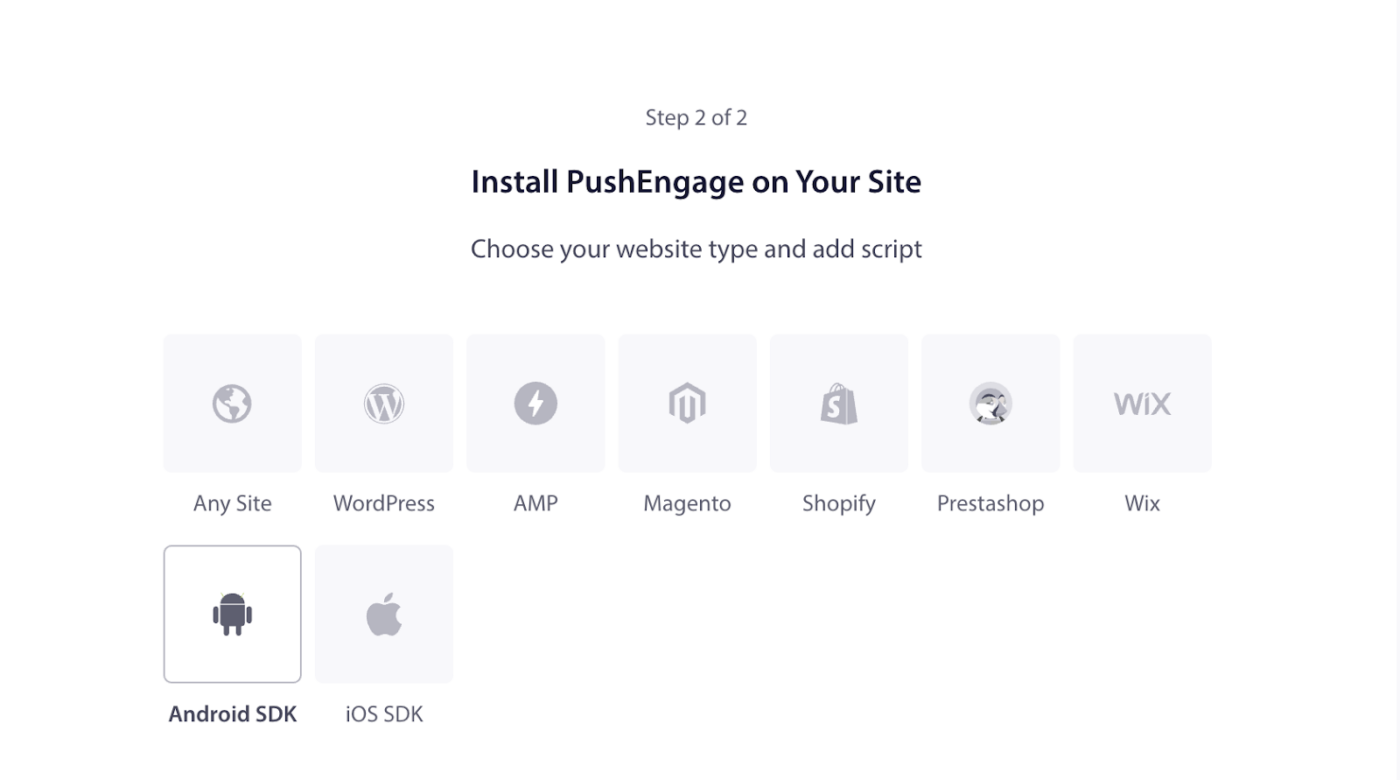
2. In the left navigation, go to Settings » Installation. Choose Android SDK
3. From the list of available platforms, choose the Android SDK option to configure push notifications for Android.
4. Configure FCM Settings – Enter your Firebase Sender ID (retrieved from the Firebase Console). Upload the Service Account JSON file (downloaded from Firebase). Click the Update button to save these settings.
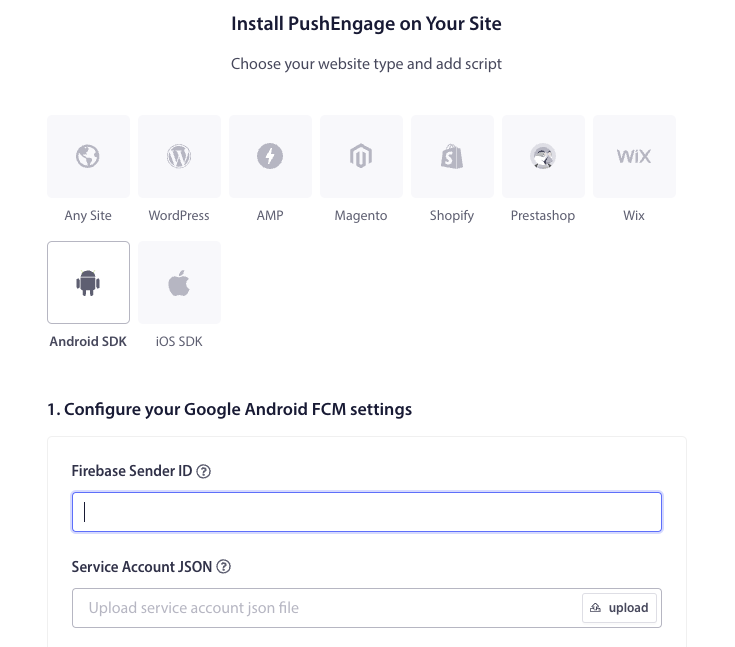
5. After configuring the FCM settings, you’ll be provided with an App ID. Copy this App ID as it is required to initialize the PushEngage Android SDK in your Flutter app.
Setting Up iOS
You can follow the steps after opening your_project_name » iOS » your_project_name.xcworkspace.
Step 1: Enable Remote Notifications
1. Open your Xcode project and select the root project in the Project Navigator.
2. Choose your main app target.
3. Navigate to “Signing & Capabilities.“
4. Ensure that Background Modes capability is added. If not, add it by clicking the “+ Capability” button.
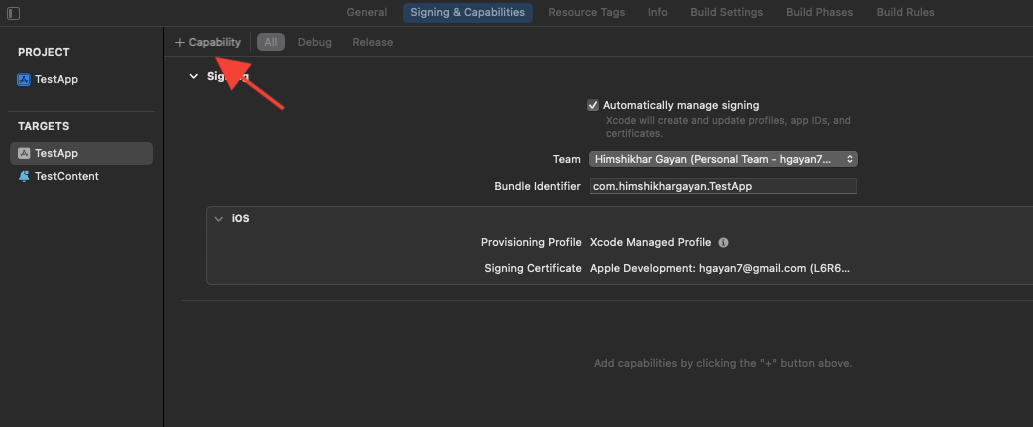
5. Similarly, ensure that the Push Notifications capability is added. If not, add it using the “+ Capability” button.
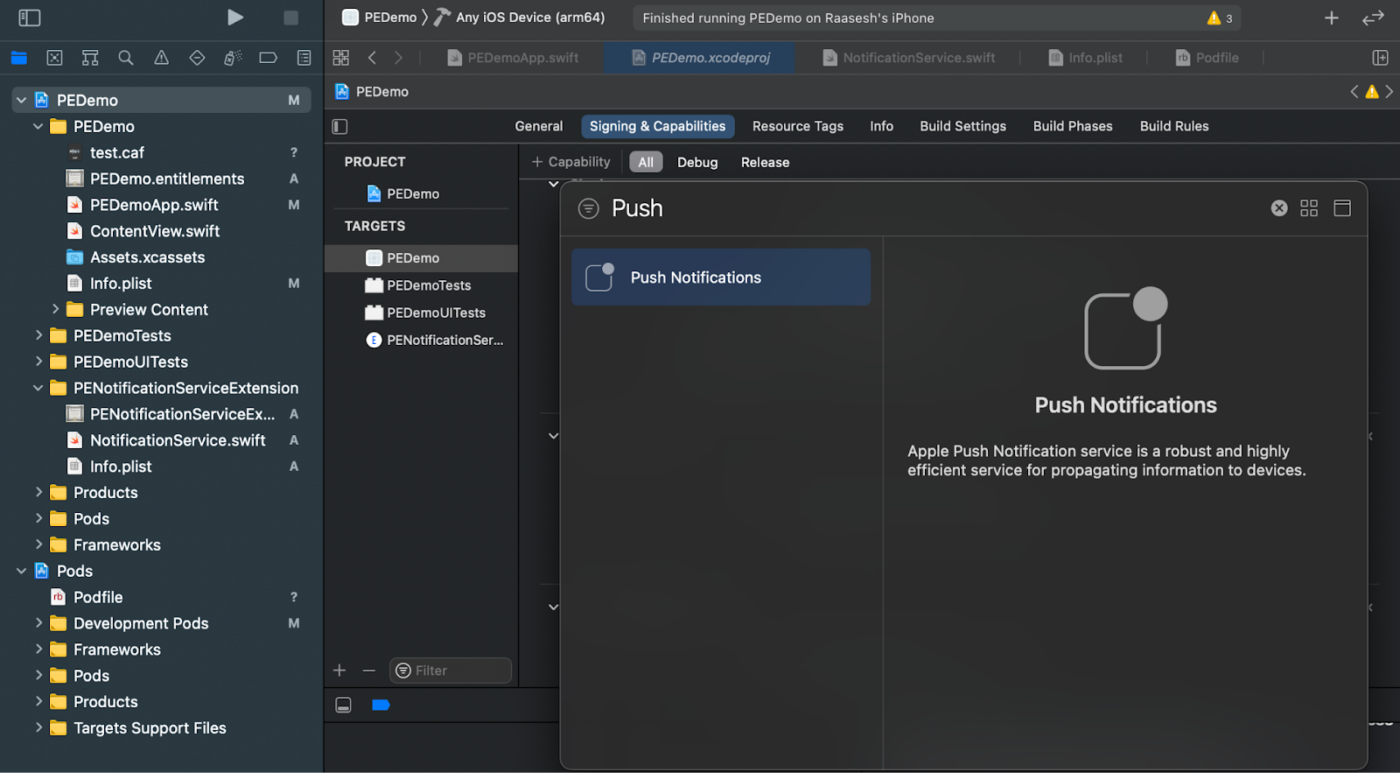
If the “Push Notifications” capability is not visible in Xcode:
1. Go to your Apple Developer account.
2. Navigate to “Certificates, Identifiers & Profiles.“
3. Select your app identifier.
4. Edit the configuration of your App ID and ensure that Push Notifications is enabled.
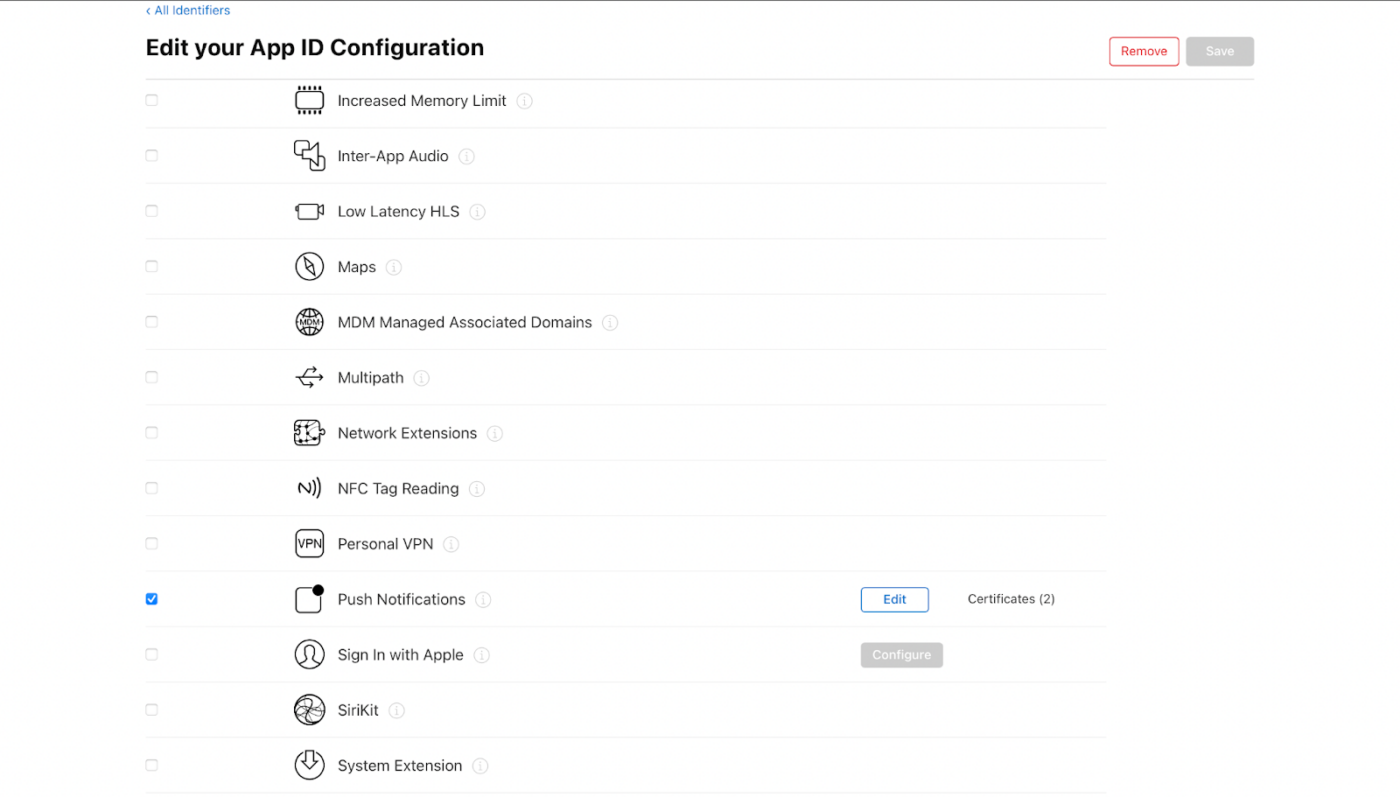
5. Return to Xcode and attempt to add the Push Notifications capability again.
Step 2: Enable Background Modes
1. In your Xcode project, navigate to “Signing & Capabilities.“
2. Inside “Background Modes“, enable both “Remote notifications” and “Background fetch.“
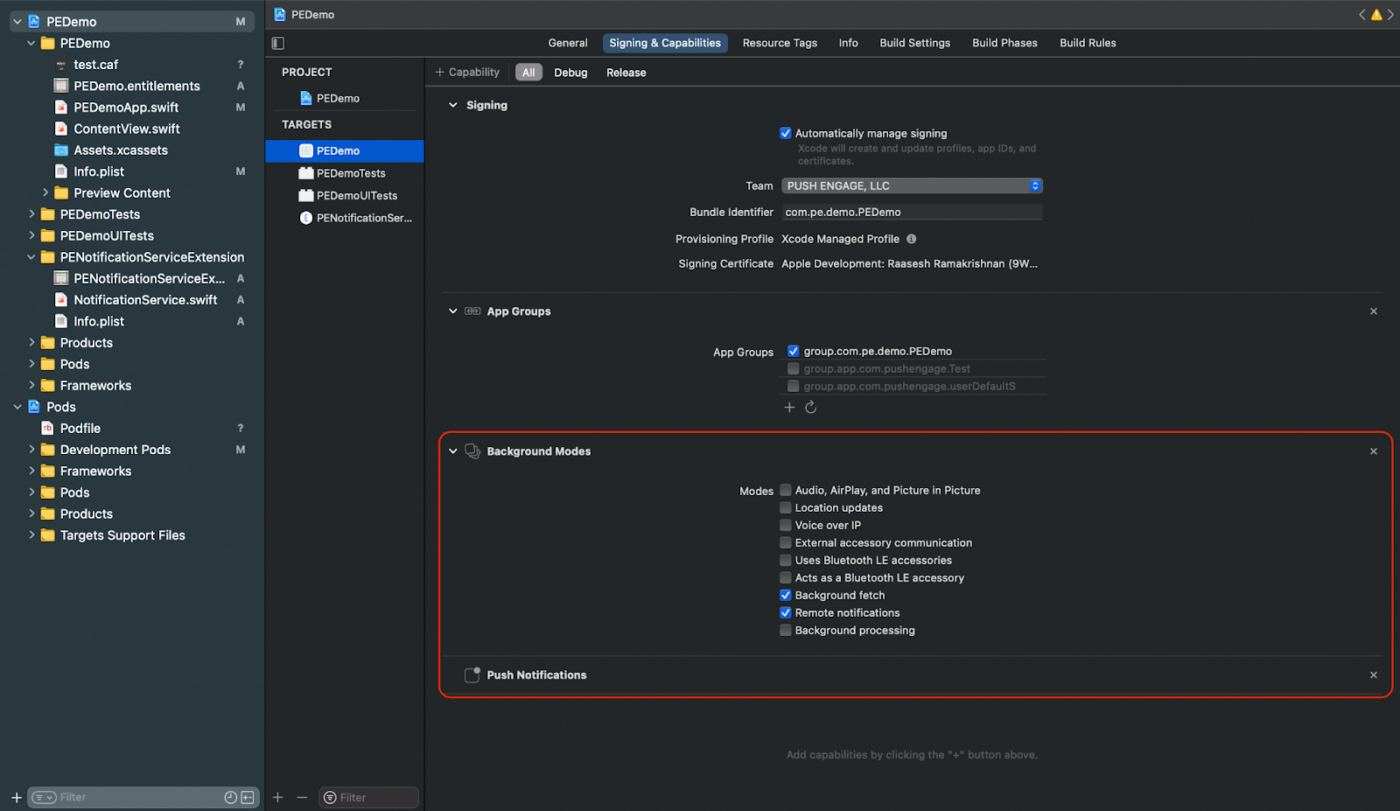
This step ensures that your app can handle remote notifications and background fetches efficiently.
Create iOS APNs certificate
You can refer to the guide here to create an iOS APNs certificate if you do not have one already.
Add Notification Service extension and Notification Content Extension
This is only applicable for iOS devices.
Creating Notification Service Extension
The Notification Service Extension enhances your iOS app’s capability to receive notifications. This is used to modify the notification’s content or fetch/process any data on receiving the notification. Follow these steps to create a Notification Service Extension:
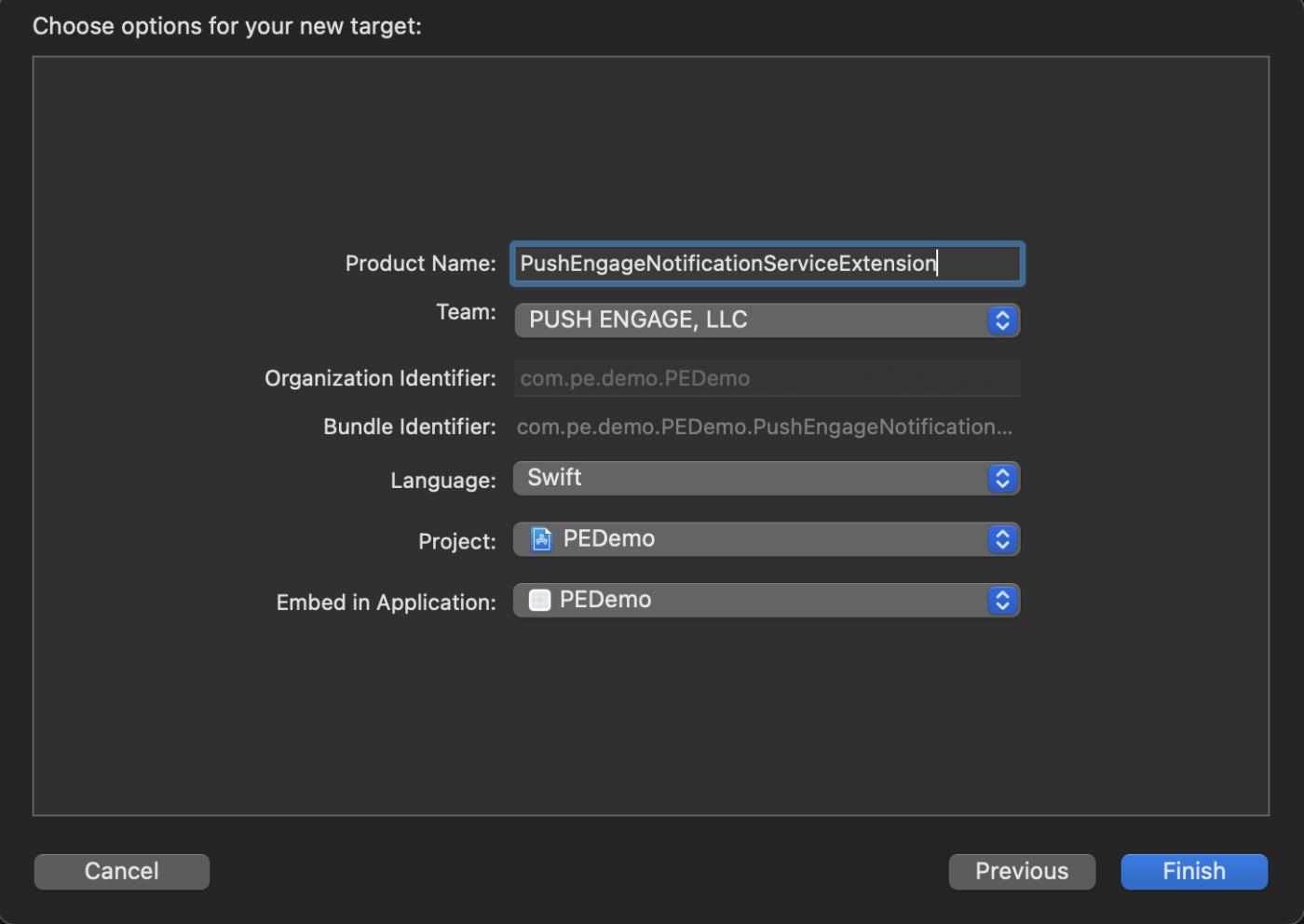
1. Open Xcode and navigate to your project.
2. Select File » New » Target from the menu.
3. In the template selection window, choose Notification Service Extension and click Next.
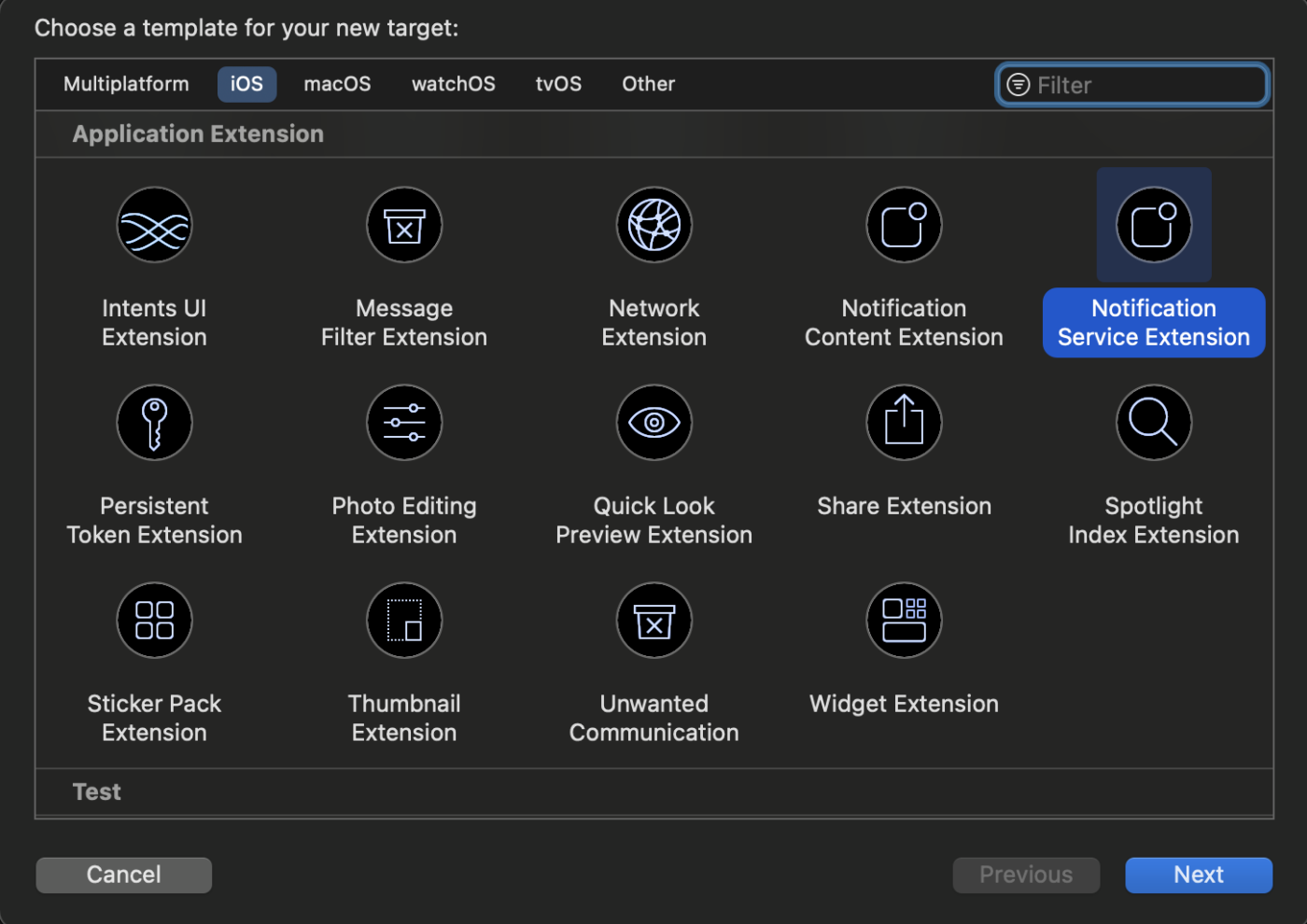
4. Provide a name for your extension, for example, PushEngageNotificationServiceExtension, and click Finish.
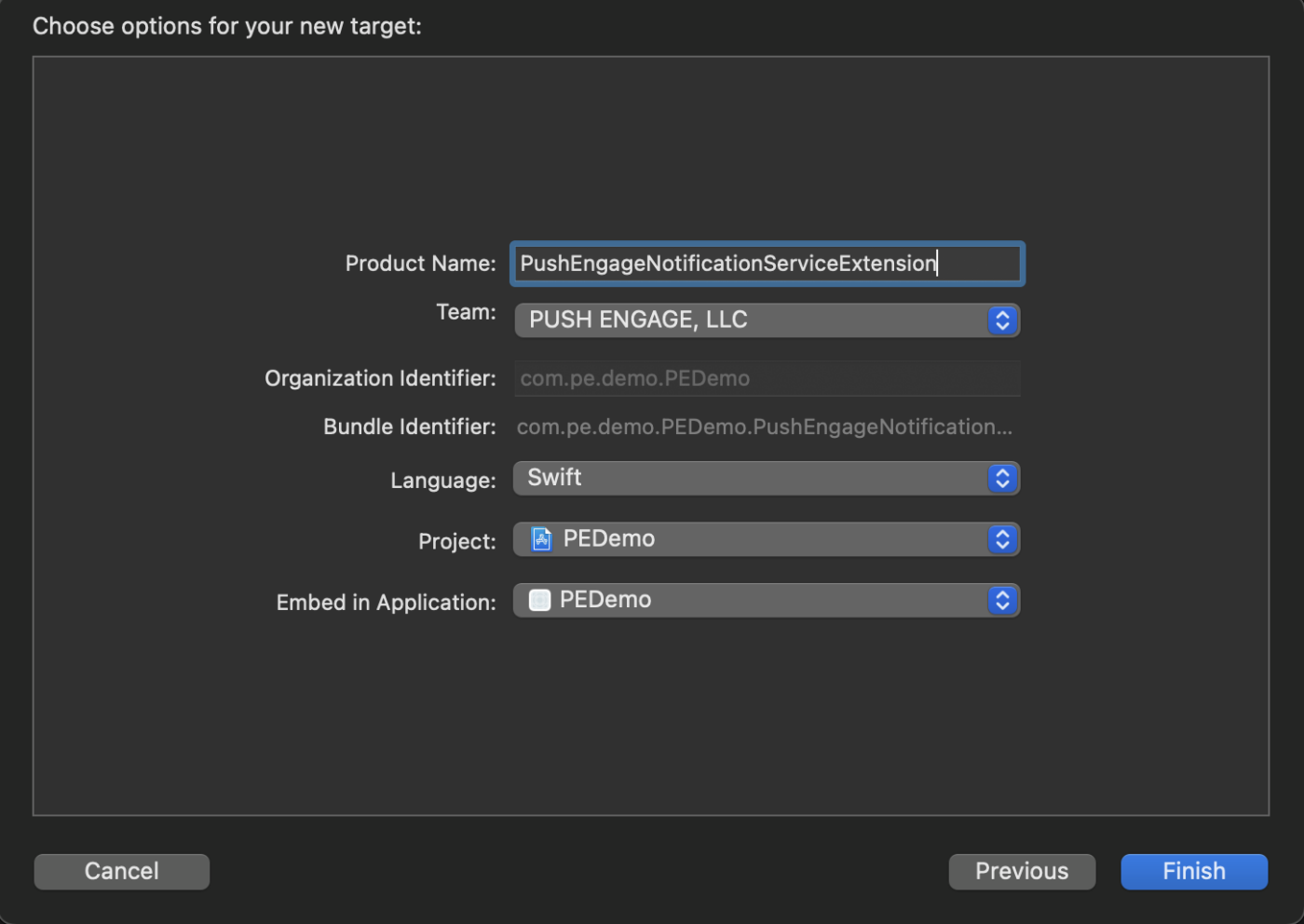
Once you finish creating the Notification Service Extension, you might be prompted to activate it. Do not activate it immediately.
Activating the extension would shift Xcode’s debugging focus from your app to the extension. If you activate it by accident, don’t worry; you can switch back to debugging your app within Xcode.
5. In the project navigator, select the top-level project directory and select the NotificationServiceExtension target in the project from the targets list created in step no. 4.
6. Set the Deployment Target to be at iOS 10 or above, which is the version of iOS that Apple released the support for this extension.
Initializing PushEngage SDK for Notification Service Extension
To ensure the proper functioning of PushEngage SDK in your iOS Notification Service Extension, follow these steps:
1. Open your_project_name » ios » Podfile.
2. Add the following to the post_install block of the main app target
post_install do |installer|
# https://github.com/facebook/react-native/blob/main/packages/react-native/scripts/react_native_pods.rb#L197-L202
react_native_post_install(
installer,
config[:reactNativePath],
:mac_catalyst_enabled => false,
# :ccache_enabled => true
)
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings['APPLICATION_EXTENSION_API_ONLY'] = 'No'
end
end
end
3. Add to the bottom of the file
target 'Your_Notification_Service_Extension_Name' do
pod 'PushEngage', '~>0.0.5'
end
4. Install the dependency
pod repo update
pod install
5. In your Notification Service Extension target, make sure to import the PushEngage framework and add the necessary initialization code.
Swift
import UserNotifications
import PushEngage
@available(iOSApplicationExtension 10.0, *)
class PushEngageNotificationServiceExtension: UNNotificationServiceExtension {
var contentHandler: ((UNNotificationContent) -> Void)?
var bestAttemptContent: UNMutableNotificationContent?
var request : UNNotificationRequest?
override func didReceive(_ request: UNNotificationRequest, withContentHandler contentHandler: @escaping (UNNotificationContent) -> Void) {
self.request = request
self.contentHandler = contentHandler
self.bestAttemptContent = (request.content.mutableCopy() as? UNMutableNotificationContent)
if let bestContent = bestAttemptContent {
PushEngage.didReceiveNotificationExtensionRequest(request, bestContentHandler: bestContent)
contentHandler(bestContent)
}
}
override func serviceExtensionTimeWillExpire() {
// Called just before the extension will be terminated by the system.
// Use this as an opportunity to deliver your "best attempt" at modified content, otherwise the original push payload will be used.
if let contentHandler = contentHandler, let request = request ,let bestAttemptContent = bestAttemptContent {
guard let content = PushEngage.serviceExtensionTimeWillExpire(request, content: bestAttemptContent) else {
contentHandler(bestAttemptContent)
return
}
contentHandler(content)
}
}
}
Creating Notification Content Extension
To improve the way by adding custom UI, you’ll need to create a Notification Content Extension. Follow the steps below to set up the extension:
1. In Xcode, go to File » New » Target.
2. Select Notification Content Extension and click Next.
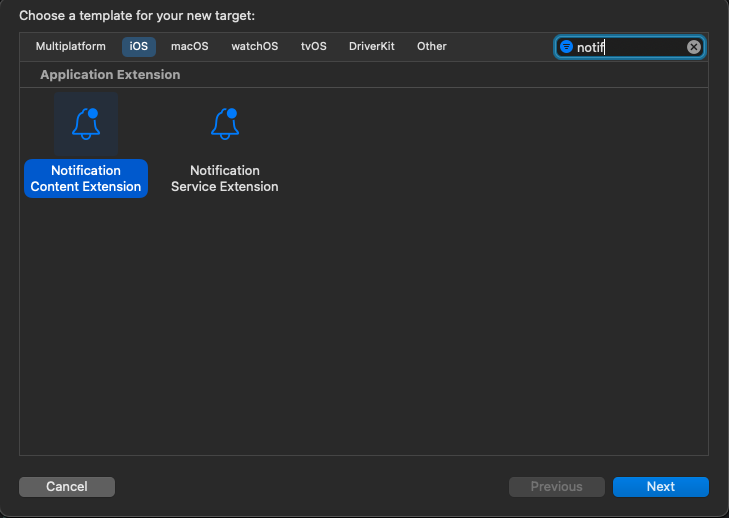
3. Do not select “Activate” on the dialog that appears after clicking Finish. Canceling keeps Xcode debugging your app instead of the extension. If you accidentally activate it, switch back to debugging your app within Xcode (next to the run button).
4. In the project navigator, select the top-level project directory and select the NotificationContentExtension target in the project from the targets list created in step no. 2.
5. Set the Deployment Target to iOS 10 or above, which is the version of iOS that Apple released the support for this extension.
Initializing PushEngage SDK for Notification Content Extension
To ensure the proper functioning of PushEngage SDK in your iOS Notification Content Extension, follow these steps:
1. Open your_project_name » iOS » Podfile.
2. Add the following in the bottom of your Podfile:
target 'Your_Notification_Content_Extension_Name' do
pod 'PushEngage', '0.0.5'
end
3. Install the dependency:
cd into the ios directory of your project and run the below command
pod repo update
pod install
4. In your Notification Content Extension target, make sure to import the PushEngage framework and add the necessary initialization code. Here’s how you can do it with some example of UI elements:
Swift
import UIKit
import UserNotifications
import UserNotificationsUI
import PushEngage
@available(iOSApplicationExtension 10.0, *)
class NotificationViewController: UIViewController, UNNotificationContentExtension {
fileprivate var hostingView: UIHostingController<ContentView>?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.view.backgroundColor = .white
}
func didReceive(_ notification: UNNotification) {
if(notification.request.content.categoryIdentifier == "your_identifier"){
let payLoad = PushEngage.getCustomUIPayLoad(for: notification.request)
//pass the payload to your custom View
let view = CustomView(payLoadInfo: payLoad)
hostingView = UIHostingController(rootView: view)
If let customView = self.hostingView {
addChild(hostingView!)
}
}
}
}
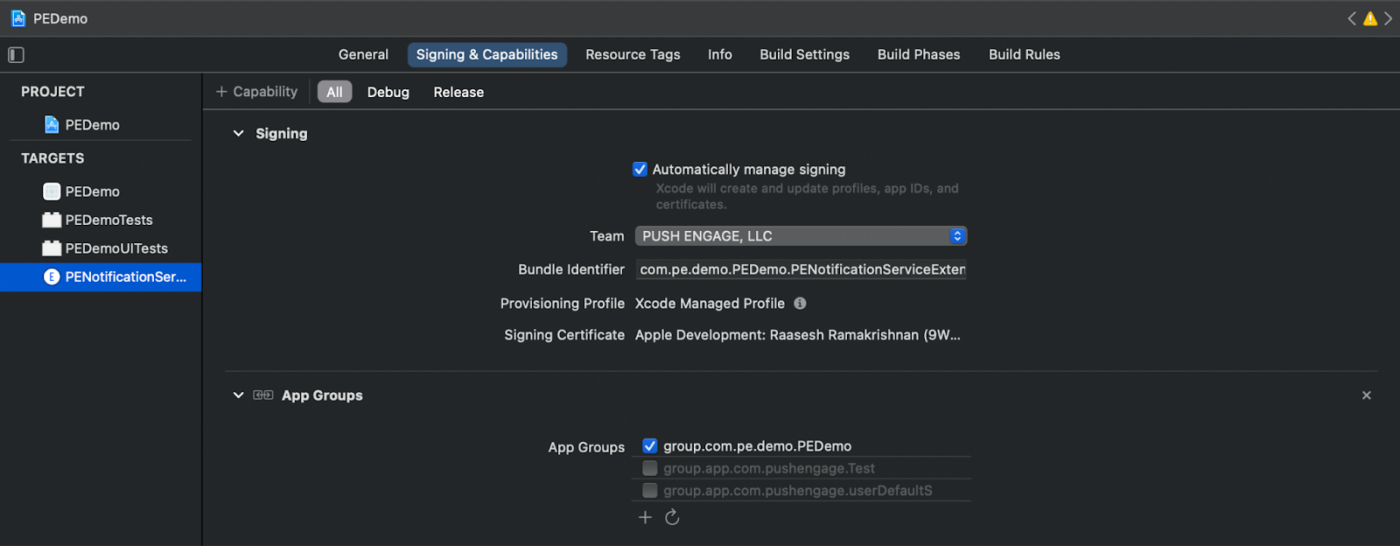
Add App Groups
App Groups are essential for enabling communication between the main app, notification service extension, and notification content extension. Follow these steps to add App Groups to your iOS project:
If you have an existing app group and wish to use the same, you can skip to step no. 4.
1. In your Xcode project, in the project navigator, select the top-level project directory and select the main target of the app.
2. Navigate to the Signing & Capabilities tab.
3. Click the “+ Capability” button and select App Groups from the list.
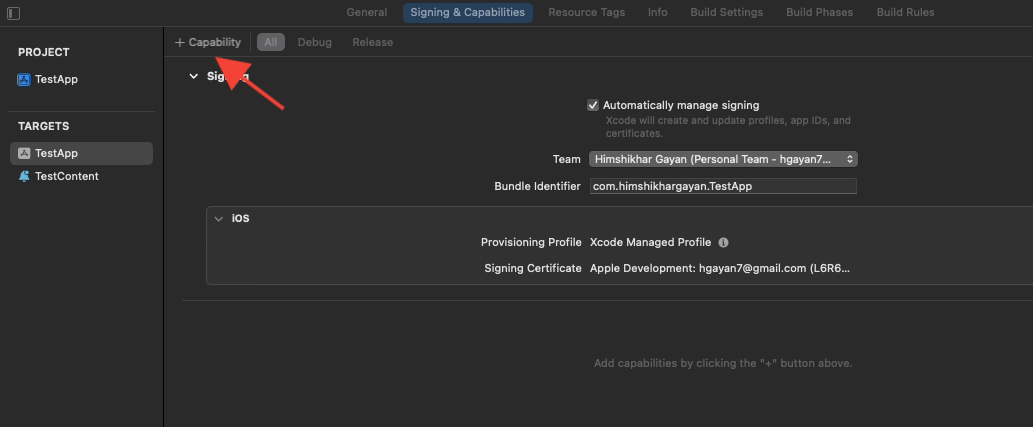
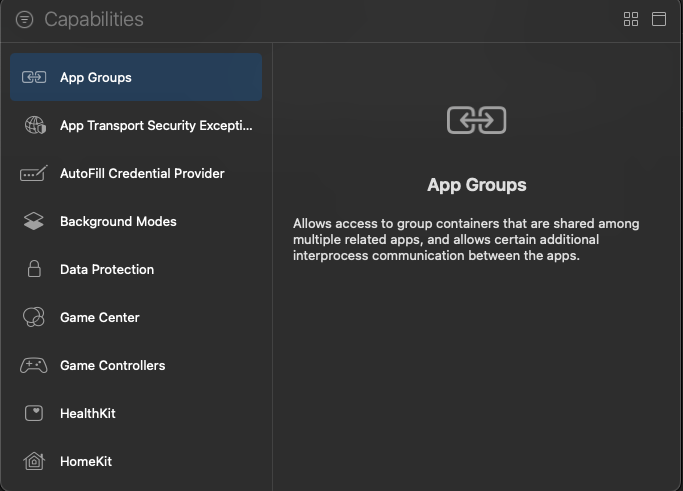
4. Click on the + button to add an App Group.
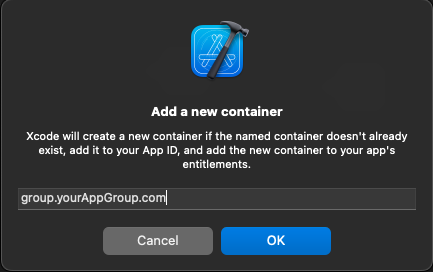
5. Add a unique name to your App Group and click on OK.
6. In the main editor area, select the main target of your app. If you have created an app group please provide the name of the group in your application Info.plist with key PushEngage_App_Group_Key.
7. Add the same key and value in the Notification Service Extension’s Info.plist file.
8. Make sure you select the same app group in both Main Application Target and the Your_Notification_Service_Extension.
Initialize PushEngage SDK
In your index.js, initialize the PushEngage SDK.
import PushEngage from 'pushengage-react-native';
PushEngage.setAppId('your-app-id');
In your AppDelegate.mm of iOS app
@import PushEngage;
@implementation AppDelegate
- (instancetype)init
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
[PushEngage swizzleInjectionWithIsEnabled: YES];
}
return self;
}
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
self.moduleName = @"PushengageReactNativeExample";
// You can add your custom initial props in the dictionary below.
// They will be passed down to the ViewController used by React Native.
self.initialProps = @{};
[PushEngage setInitialInfoFor:application with:launchOptions];
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
- (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification:(NSDictionary *)userInfo fetchCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UIBackgroundFetchResult))completionHandler {
completionHandler(UIBackgroundFetchResultNewData);
}
Handling deepLink
Listen for deep link events and handle them in your application
const listenerSubscription = React.useRef<null | EventSubscription>(null);
React.useEffect(() => {
listenerSubscription.current = PushEngage.onValueChanged((data) => {
Alert.alert(`Deeplink: ${data.deepLink}`);
console.log('Data:', data.data);
});
return () => {
listenerSubscription.current?.remove();
listenerSubscription.current = null;
};
}, []);
Troubleshooting
Add -fcxx-modules in Other C++ flags for error: use of ‘@import’ when c++ modules are disabled, consider using -fmodules and -fcxx-modules under iOS project’s Build Settings.
If you want to explore more of the capabilities of iOS SDK, you can go through our detailed API documentation.
If you run into any issues, please contact us by clicking here. Our support team will be able to help you.